Vitamin D Deficiency
The Statesman
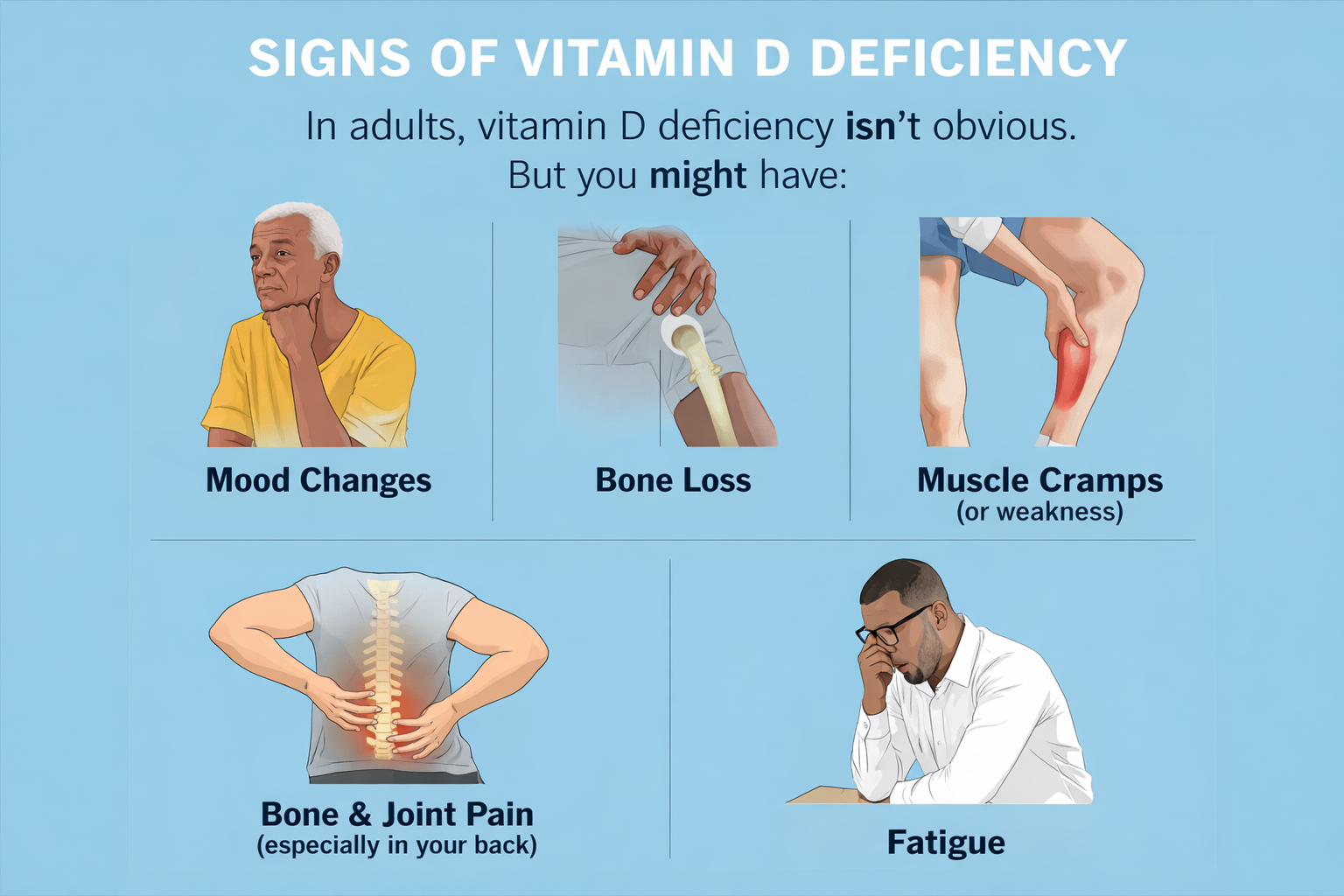
Key Arguments of the Article
- Vitamin D Deficiency as a Public Health Crisis:
The article discusses the growing issue of Vitamin D deficiency in India, highlighting a recent report from the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations. The deficiency is linked to a range of health problems, particularly bone health issues such as osteoporosis, fractures, and long-term disability. A startling statistic reveals that among children aged 10 years and below, 60-90% suffer from Vitamin D deficiency, raising the risk of fractures. - Historical Context and Discovery of Vitamin D:
The article explains the history of Vitamin D discovery during the 19th century, when scientists first identified its role in preventing rickets. Over time, the understanding of Vitamin D’s importance expanded, linking it to overall bone health and immune function. Despite these advancements, Vitamin D deficiency remains a widespread issue, especially in developing countries like India. - Modern-Day Causes of Deficiency:
Several factors contribute to the widespread Vitamin D deficiency in India, including insufficient sun exposure, poor dietary habits, and a high prevalence of indoor lifestyles. Despite living in a country with abundant sunlight, many people avoid direct exposure due to the heat, and modern living conditions, such as sedentary indoor jobs, contribute to the deficiency. - Effects of Vitamin D Deficiency:
Vitamin D deficiency is tied to numerous health concerns, including rickets in children, osteoporosis in adults, and a weakened immune system. The deficiency also plays a role in several chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. The deficiency has broader public health consequences, especially as it affects a significant portion of the population. - Remedies and Solutions:
The article suggests several methods for addressing Vitamin D deficiency, including increased sunlight exposure, dietary changes to include foods rich in Vitamin D (such as dairy, fish, and fortified cereals), and the use of Vitamin D supplements. Public health campaigns and education about the importance of Vitamin D are recommended, as well as better healthcare access to diagnose and treat the deficiency.
Author’s Stance and Potential Biases
- Factual and Informative:
The article maintains a largely factual and informative tone, presenting scientific evidence from both historical and modern sources to explain the significance of Vitamin D and its role in public health. However, it lacks in-depth analysis of the reasons behind the persistent public health crisis, focusing instead on medical and preventive aspects. - Implicit Critique of Public Health Policies:
While not overtly critical, the article implicitly critiques India’s public health infrastructure and awareness programs. The failure to effectively address Vitamin D deficiency, despite the country’s abundance of sunlight, suggests shortcomings in health education, accessibility to healthcare, and dietary awareness. - Emphasis on a Medicalized View:
The article focuses primarily on the medical implications of Vitamin D deficiency and its treatment through supplements and dietary changes. While this is appropriate, it could benefit from a more comprehensive approach that includes socio-cultural factors and systemic barriers to improving public health.
Structured Analysis of the Article
Pros:
- Clear and Accessible Information:
The article effectively conveys the critical public health issue of Vitamin D deficiency, breaking down complex scientific concepts into simple terms that can be understood by a wide audience. It also provides relevant statistics, making the issue tangible and urgent. - Historical Context:
The inclusion of historical context surrounding the discovery of Vitamin D provides an informative backdrop, highlighting the importance of this nutrient in maintaining bone health and preventing diseases like rickets. - Call to Action:
The article offers actionable suggestions for combating Vitamin D deficiency, including increased sunlight exposure, dietary changes, and healthcare intervention. It helps raise awareness on how individuals can take preventive measures.
Cons:
- Limited Exploration of Socio-Cultural Factors:
While the article touches on some of the causes of Vitamin D deficiency, it does not delve into the deeper socio-cultural factors that contribute to the crisis. For example, factors like dietary patterns influenced by culture, economic barriers to accessing supplements, and the high urbanization rate limiting outdoor activity are not explored in detail. - Lack of Policy Discussion:
The article does not address potential policy measures or initiatives that the government or public health organizations could take to address the issue on a national scale. Public health infrastructure and policies around nutrition, healthcare access, and education are not mentioned in any meaningful way. - Over-reliance on Medical Solutions:
The article’s heavy focus on medical solutions (such as supplements and dietary changes) overlooks the potential for broader public health campaigns, urban planning strategies, and government intervention that could address the root causes of Vitamin D deficiency.
Policy Implications:
- Public Health Infrastructure:
India’s health infrastructure may need significant reforms to address widespread deficiencies like Vitamin D deficiency. This could include better access to healthcare, public health education, and supplementation programs. Initiatives like free or subsidized Vitamin D supplements for low-income populations could help address the crisis. - Nutrition and Education Policies:
There is a clear need for enhanced education around nutrition, including the importance of Vitamin D. This could be integrated into school curricula, community programs, and public health campaigns. Additionally, the government may consider introducing regulations on food fortification with Vitamin D to ensure the population receives adequate levels. - Urban Planning and Social Change:
As urbanization continues, efforts should be made to encourage outdoor activity. Public spaces, parks, and recreational areas could be developed in urban areas to promote physical activity and sun exposure, particularly in highly urbanized areas where people tend to remain indoors.
Real-World Impact:
- Immediate Health Impact:
In the short term, addressing Vitamin D deficiency can have significant health benefits, reducing cases of rickets, osteoporosis, and chronic diseases like diabetes. This will improve overall public health and reduce healthcare costs in the long run. - Long-Term Societal Impact:
By tackling the root causes of Vitamin D deficiency, India can improve its population’s long-term health outcomes. Reducing preventable diseases through proper nutrition and healthcare interventions can boost productivity, reduce the burden on the healthcare system, and enhance overall quality of life.
Relevance to UPSC GS Papers:
- GS Paper II – Governance, Polity, and Social Justice:
The article ties into public health governance and the role of government in addressing nutrition-related public health issues. It calls attention to the importance of effective public health infrastructure and education policies in tackling widespread health crises like Vitamin D deficiency. - GS Paper II – Health and Education:
The article aligns with discussions on health policy and its impact on the population’s well-being. The emphasis on dietary changes and public health measures directly ties into topics related to nutrition, healthcare systems, and their importance in achieving sustainable development goals. - GS Paper I – Social Issues:
Vitamin D deficiency is a significant social issue that has wide-reaching effects on public health. The article touches upon how this issue impacts various sectors, such as healthcare, the economy, and social well-being, making it relevant to social justice themes in the UPSC syllabus.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives:
The article highlights a pressing public health issue in India, drawing attention to the alarming rates of Vitamin D deficiency. While it offers valuable information on the causes, effects, and potential remedies, a more comprehensive discussion is needed to address the socio-economic and cultural barriers to addressing this issue on a national scale.
Going forward, the government and public health organizations must consider a more holistic approach, integrating policy reform, public health campaigns, and social support systems to combat this silent epidemic. Public health infrastructure must be strengthened to ensure that citizens have access to necessary supplements, preventive care, and education on proper nutrition. Through a combined effort, India can address Vitamin D deficiency and improve the overall health of its population.
